Deconstructing Operations and Maintenance in Solar O&M
Solar operations and maintenance fit together like hand and glove. Yet to ensure top performing solar PV plants, it is important to deconstruct the two items, to fully understand what each piece brings to the table, and how they best fit together to maintain your solar assets.
Solar operations can be divided into two distinct parts: Plant Operations and Field Operations. Each has a distinct role to play in troubleshooting problems and finding answers.
Plant Operations
The “O” in Solar O&M addresses Plant Operations which is critical to the continued optimum performance of the plant and consists of the following:
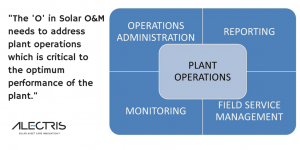 Plant Monitoring
Plant Monitoring
- Data acquisition & storage
- Online data to additional data center
- Historical data import
- Reporting
- Availability and PR calculation
- Meters readings
- Preventive maintenance services
- Base case scenario comparison/other KPIs at owner’s discretion
- Main Incidents Recorded
- Incident Root Cause Analysis
- Detection of incident causes
- Periodic evaluation of data
- Plant’s specific knowledge base
- Drafting and proposal of action plans
- Video Surveillance & Security
- Video surveillance over the system & central room surveillance monitoring
- Local security service
- Logging (alarms & access control)
- Security Incident Analysis & Reporting
- Analysis of recurring security incident
- Reporting to the owner
- Proposal of curing actions
- Principal Access to Monitoring Interface
- Availability of a full set of dashboards for continuous plant’s monitoring
- Internet Connection/Communications Monitoring
- Monitoring of connection quality
- Plant-Specific Spare Parts List
- Creation of a plant’s specific spare parts list
- Continuous updating
- Spare Parts Management
- Warehousing of spare parts (modules, inverters, fuses, etc.)
- On site transportation
- Materials Planning/Purchasing (on behalf of plant owner)
- Definition of a minimum order quantity of spare parts in agreement with the owner
- Source and ordering of spare parts
- Reordering of spare parts as soon as the minimum order quantity is reached
- Follow-up Warranties for Plant Components
- Warranty/guarantees management
- Proposal of warranty extensions
- Negotiation with the suppliers
Field Operations
The O in O&M referred to Field Operations. This is but a small part of the “O” in O&M. Field Operations consists of the following:
- Scheduling dispatch
- Identifying the appropriate technician to address the issue
- Isolating and fixing the issue
- Documenting actions taken
- Reporting and Invoice for the service call
 Difference between Operations and Maintenance
Difference between Operations and Maintenance
While the operations side consists of problem identification and solving, the maintenance piece implements the strategy. Once they are given the work order, the maintenance team can physically address the problem.
Proper maintenance relies heavily on the information provided by both the plant and field operations. It is the last piece in a pyramid that begins with a large base of data and hones that into a targeted strategy.
Laks Sampath, Alectris Country Manager for the U.S. and Latin America, states “Plant operations is very different from plant maintenance. It’s very important to start asking, ‘Who does the plant operations? How is it done? What are the guarantees you can provide?’”
Best Practices of Solar Operations and Maintenance
- Clearly defined parameters
- Streamlined monitoring systems
- Actionable analytics
- Targeted problem solving
I. Defining Parameters for Solar Operations and Maintenance
The key to efficient operations is to have clearly defined parameters, so they can be monitored effectively. It is imperative to understand exactly what the plant is supposed to do. In order for operations to assess whether the plant is performing to its optimal standards they must know exactly what they are.
Once the parameters are in place interpreting monitored data into useful information becomes much simpler. New technologies streamline the process even further. Monitoring plants by looking at charts was once an industry norm, but software programs such as the Alectris ACTIS platform increase efficiency and reduce cost.
Where root cause analysis was once a tedious process that required intensive scrutiny, ACTIS now takes on the role of sifting through the data. It alerts the team when it identifies a deviation from the norm. Now the team can spend more time reviewing the anomalies to determine whether the alert requires action. If so, the team can then focus its efforts on determining the best course of action.
II. Using Asset Management Software to Streamline Solar PV Monitoring
The Alectris ACTIS software platform allows its users to program the system to ignore anomalies that are related to the actual operations of the plant.
For example, if the team is aware that during certain times a particular sector will not be operating at its full capacity due to shading or other issues, the system will not report those decreased outputs.
Another area that is streamlined by the ACTIS platform is spare parts management. This can be a nightmare for many organizations, but it doesn’t have to be if managed properly. The ACTIS program maintains a database of all the equipment that is used at the plant, as well as spare-parts location and quantity.
It can be programmed to set thresholds at which new parts must be ordered, which ensures that the plant will never run out of parts. If needs change over time, the database can easily be updated.
Thus, strong asset management software can also provide a bridge between the two sides of operations.
III. Actionable Solar PV Analytics
This process is known as actionable analytics. The software is programmed to determine which anomalies are reportable, saving time. When plant operations receive and analyze data it determines the best course of action. In some cases, this may turn out to mean that no further action is warranted.
At this point, the process goes no further. Plant operations team will not create a service order to send to field operations, and the maintenance crews won’t be deployed. The fewer teams that need to be involved, the greater the savings of time, resources, and money.
When action is warranted, the plant operations team needs to be able to provide a precise and specific area for the field operations team to target their efforts.
IV. Targeted Problem Solving
Once field operations receives a service ticket, having problem solving systems in place is key. When the team has a blueprint to guide their problem solving strategy, they can forward a work order to maintenance more quickly. This allows maintenance to bring the plant back up to its full potential faster, increasing efficiency and cost effectiveness.
The same principle applies when spare parts management is automated. Fewer personnel resources are used, less time is spent in trying to locate parts, and plant operations are not disrupted due to missing parts.
It is clear that while operations and maintenance are influenced by each other, each has its own separate and essential role to play in ensuring the plant will perform to its highest standards.
